What is P Value How to interpret and calculate P Value YouTube
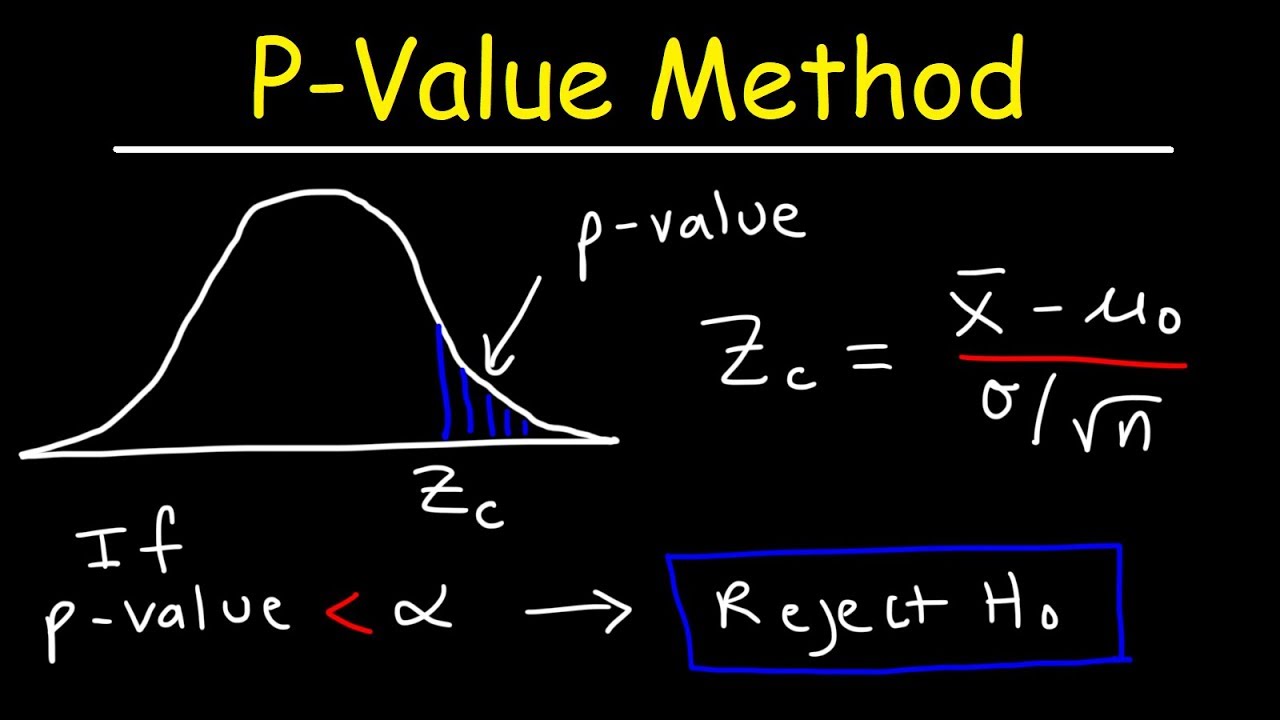
PValue Method For Hypothesis Testing YouTube
A p-value, or probability value, is a number describing how likely it is that your data would have occurred by random chance (i.e., that the null hypothesis is true). The level of statistical significance is often expressed as a p-value between 0 and 1. The smaller the p -value, the less likely the results occurred by random chance, and the.

What Does P Value Mean
P-Value: The p-value is the level of marginal significance within a statistical hypothesis test representing the probability of the occurrence of a given event. The p-value is used as an.
P Value Definition, Formula, Table, Finding Pvalue, Significance
These are as follows: if the P value is 0.05, the null hypothesis has a 5% chance of being true; a nonsignificant P value means that (for example) there is no difference between groups; a statistically significant finding (P is below a predetermined threshold) is clinically important; studies that yield P values on opposite sides of 0.05.

Understanding PValues and Statistical Significance
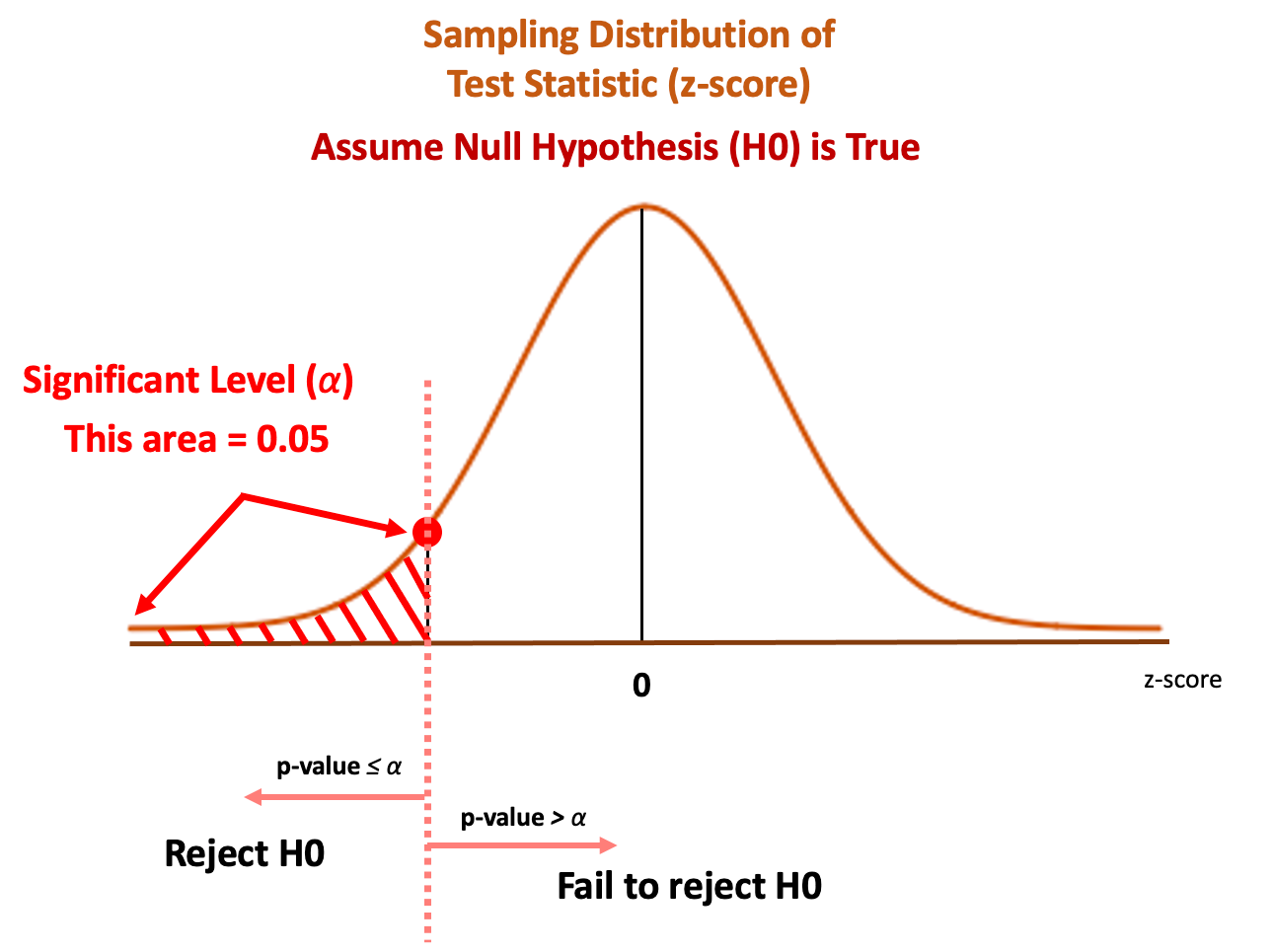
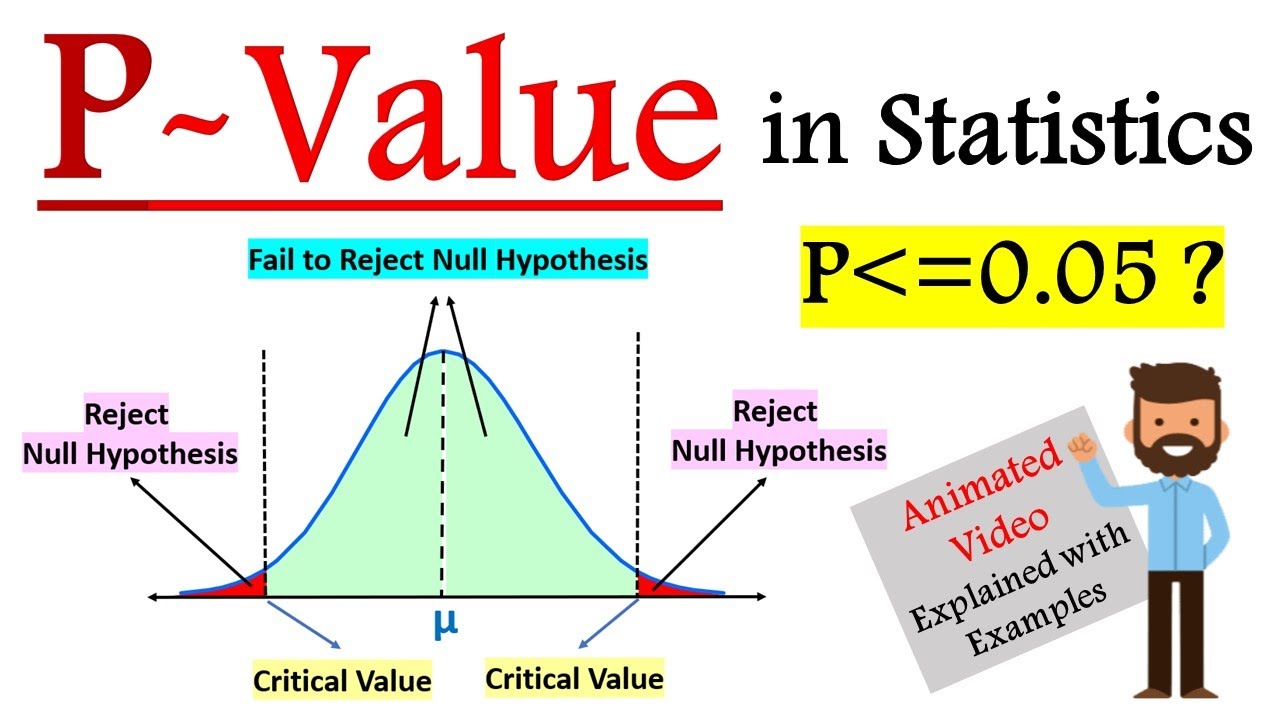
It is the cutoff probability for p-value to establish statistical significance for a given hypothesis test. For an observed effect to be considered as statistically significant, the p-value of the test should be lower than the pre-decided alpha value. Typically for most statistical tests (but not always), alpha is set as 0.05.
What is the pvalue?. Detailed explanation of pvalue by ChiaYun
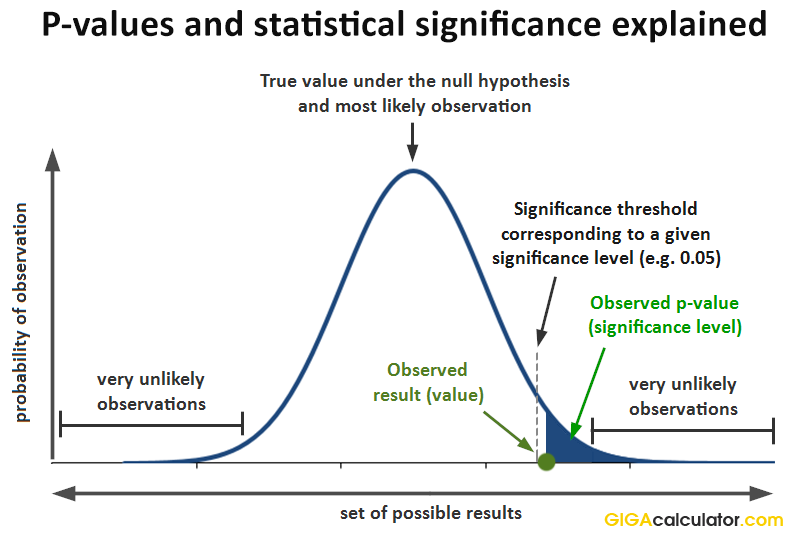
The textbook definition of a p-value is: A p-value is the probability of observing a sample statistic that is at least as extreme as your sample statistic, given that the null hypothesis is true. For example, suppose a factory claims that they produce tires that have a mean weight of 200 pounds. An auditor hypothesizes that the true mean weight.
Pvalue Definition, Significance, Formula, Table, Finding Pvalue
The p value is the evidence against a null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis. P values are expressed as decimals although it may be easier to understand what they are if you convert them to a percentage. For example, a p value of 0.0254 is 2.54%.
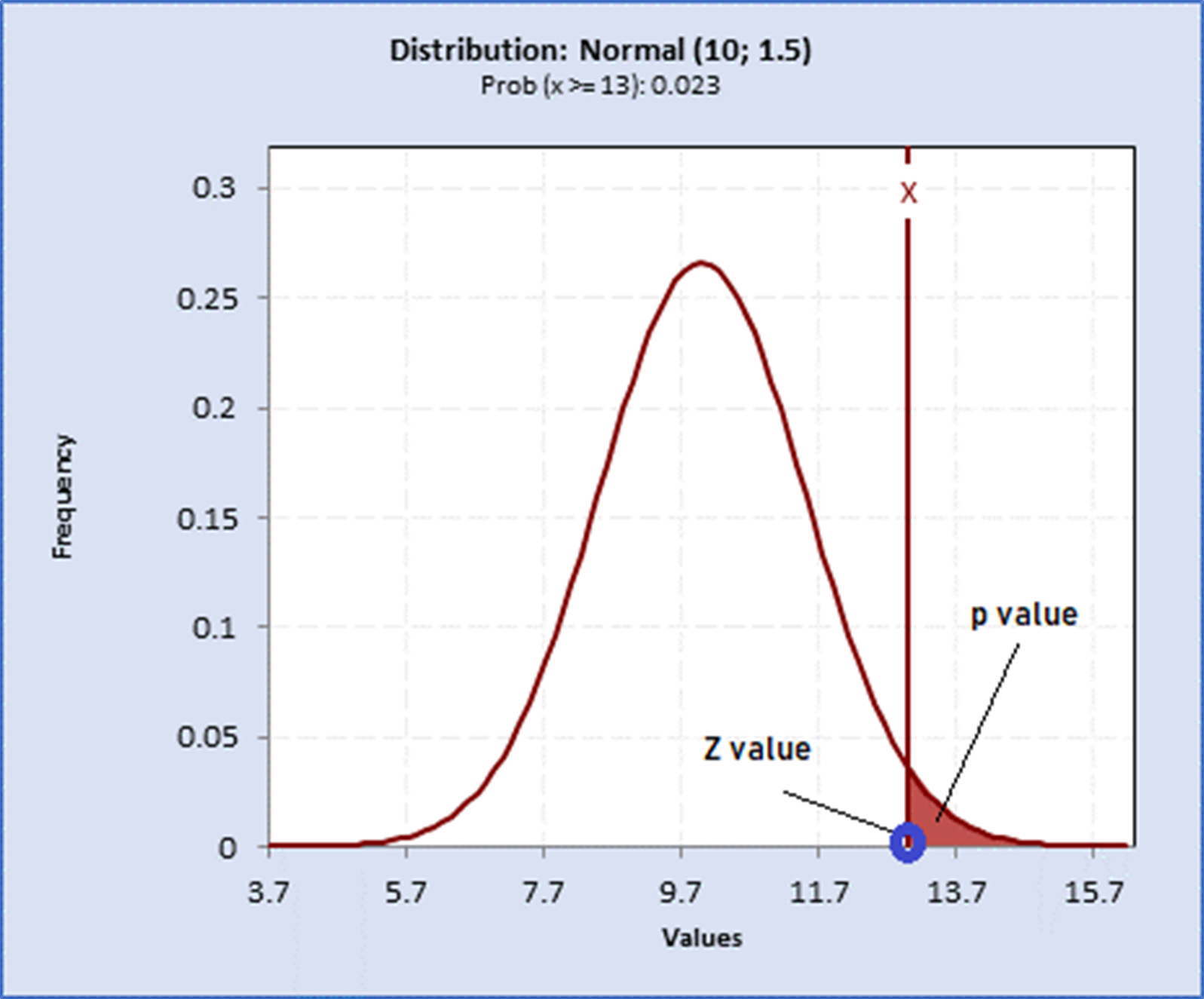
Working with p values in data analysis Blogs Sigma Magic
The p-value is the probability of the observed data given that the null hypothesis is true, which is a probability that measures the consistency between the data and the hypothesis being tested if, and only if, the statistical model used to compute the p-value is correct ( 9 ). The smaller the p-value the greater the discrepancy: "If p is.
PPT Understanding Pvalues and Confidence Intervals PowerPoint
The height coefficient in the regression equation is 106.5. This coefficient represents the mean increase of weight in kilograms for every additional one meter in height. If your height increases by 1 meter, the average weight increases by 106.5 kilograms. The regression line on the graph visually displays the same information.

What is P Value How to interpret and calculate P Value YouTube
p-value = 2 × min{Pr(S ≤ x | H 0), Pr(S ≥ x | H 0)} (By min{a,b}, we denote the smaller number out of a and b.). For example, imagine we studied the effect of a new drug and got a p-value of 0.03. This means that in 3% of similar studies, random chance alone would still be able to produce the value of the test statistic that we obtained
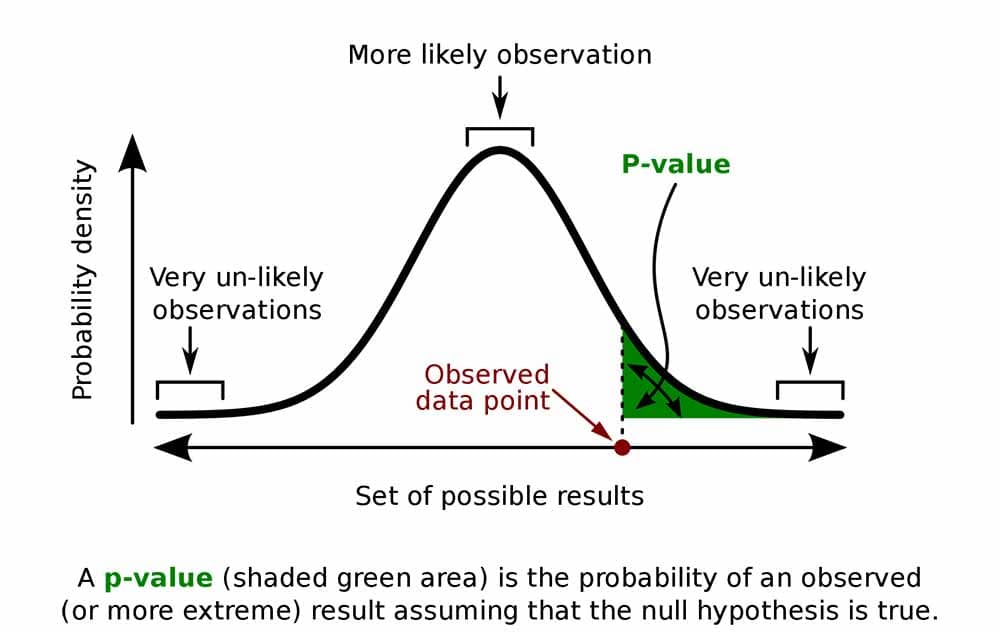
Understanding PValues and Statistical Significance
The p value gets smaller as the test statistic calculated from your data gets further away from the range of test statistics predicted by the null hypothesis. The p value is a proportion: if your p value is 0.05, that means that 5% of the time you would see a test statistic at least as extreme as the one you found if the null hypothesis was true.
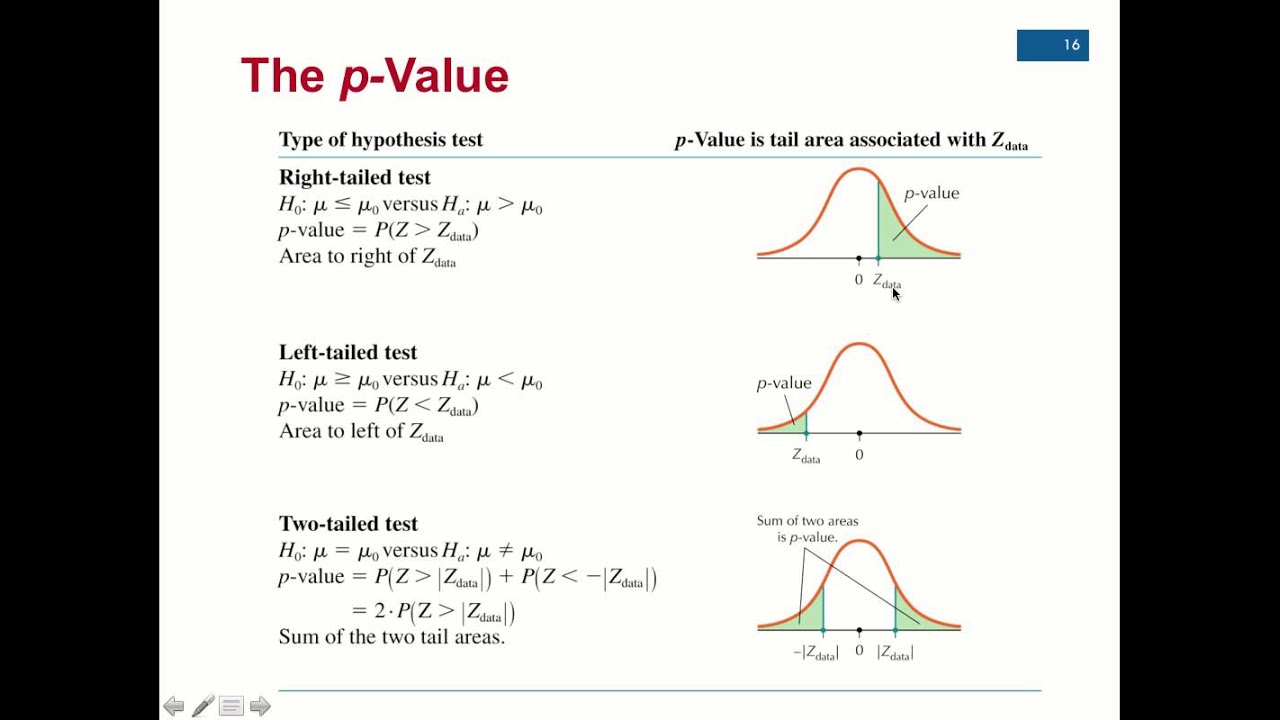
Calculating P Value
Similarly, a p value of 0.5 means that there is 5% chance that the results are due to random chance. Lower p values show more certainty in the result. To make a decision based on p values, we need to set a confidence level which indicates how sure we want to be of the results. If we set the confidence level as 95%, the significance value is 0..
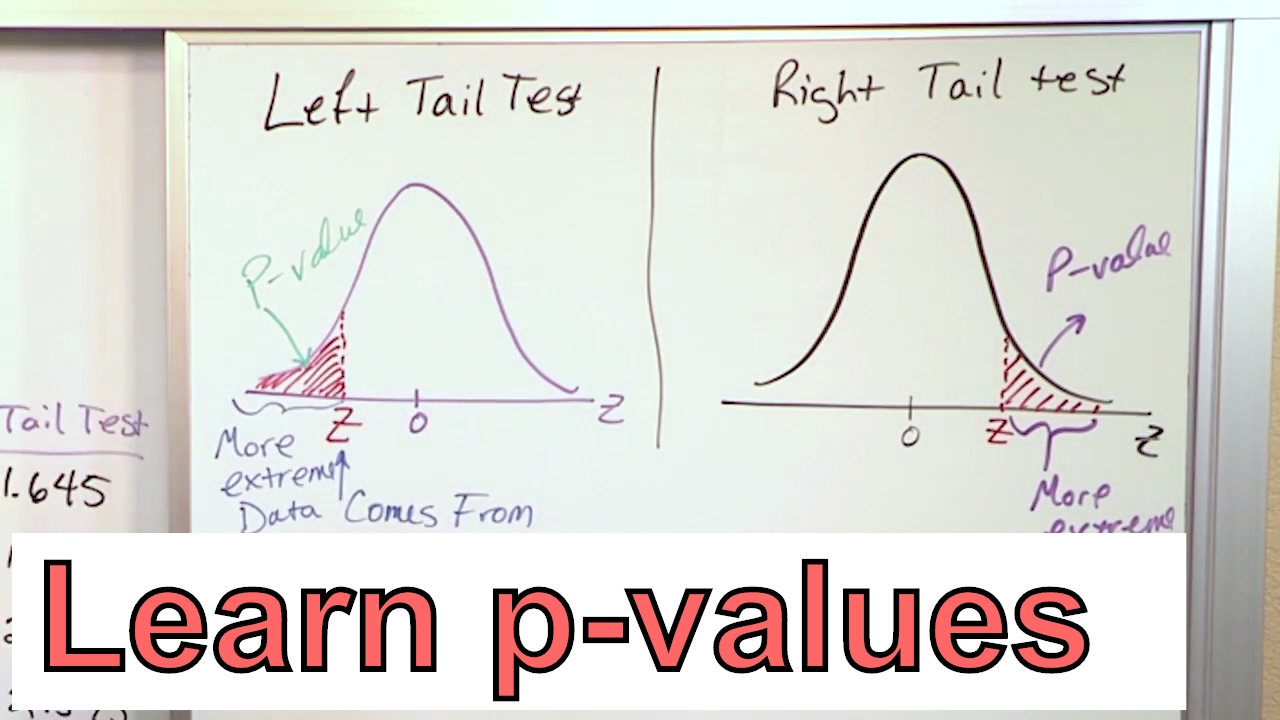
Calculate the PValue in Statistics Formula to Find the PValue in
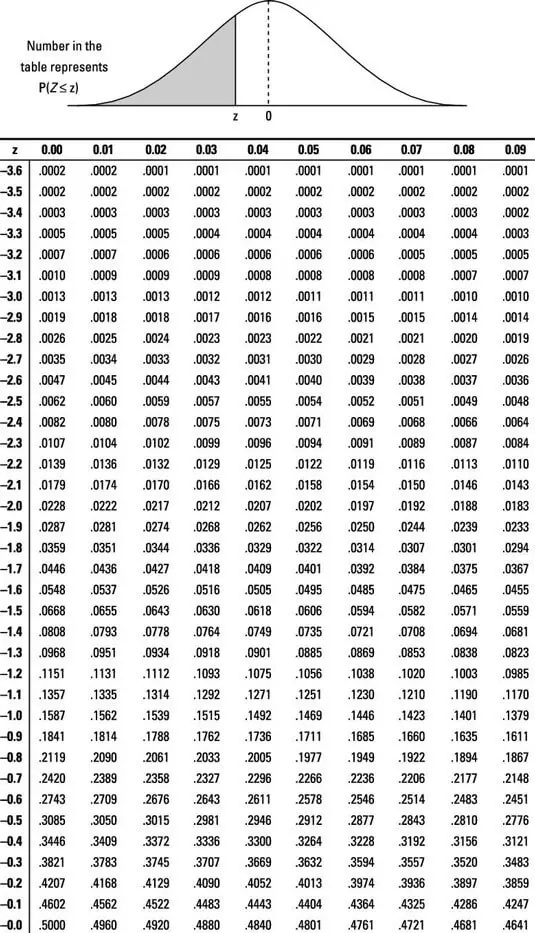
The test statistic is, therefore: Z = p ^ − p 0 p 0 ( 1 − p 0) n = 0.853 − 0.90 0.90 ( 0.10) 150 = − 1.92. And, the rejection region is: Z P lesson 9.3 α = 0.05 -1.645 0 0.90. Since the test statistic Z = −1.92 < −1.645, we reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence at the α = 0.05 level to conclude that the rate has.
What is Pvalue in hypothesis testing PValue Method Hypothesis
The p-value 0.03 means that there's 3% (probability in percentage) that the result is due to chance — which is not true. People often want to have a definite answer (including me), and this is how I got myself confused for a long time to interpret p-values. A p-value doesn't *prove* anything.
The p value definition and interpretation of pvalues in statistics
This limitation leads us into the next section to cover a very common misinterpretation of P values. P Values Are NOT the Probability of Making a Mistake. Incorrect interpretations of P values are very common. The most common mistake is to interpret a P value as the probability of making a mistake by rejecting a true null hypothesis (a Type I.

How to calculate pvalues YouTube
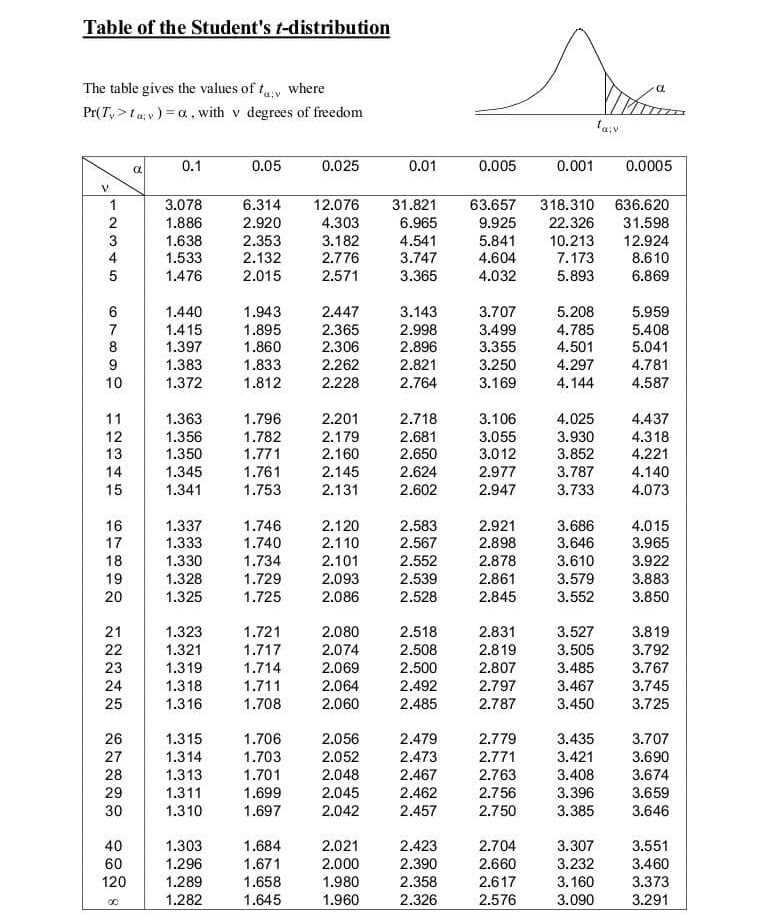
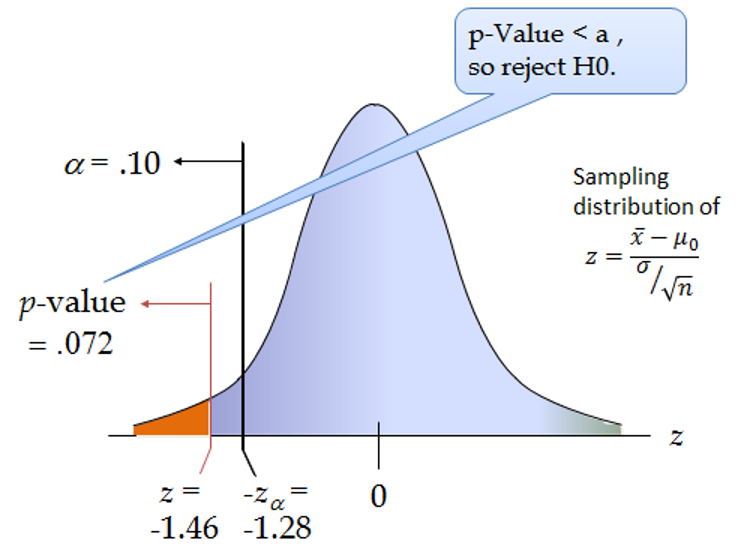
The P-value for conducting the left-tailed test H 0: μ = 3 versus H A: μ < 3 is the probability that we would observe a test statistic less than t* = -2.5 if the population mean μ really were 3. The P-value is therefore the area under a t n - 1 = t 14 curve and to the left of the test statistic t* = -2.5.
pValue in Hypothesis Testing Finance Train
Assuming that the null hypothesis is true, and p = 0.25, the sampling distribution of sample proportion with n = 60 should be approximately normal, with a mean = p = 0.25 and standard deviation of √((p·(1-p))/n) ≈ 0.056. So a sample with p-hat = 0.3 should only have a z-score ≈ 0.89, and there should be ≈ 0.187 probability of getting a.