Bones Biology 3 with Dr.j at Pasadena City College StudyBlue

MR image showing bone marrow edema of the medial femur condyle with a
Bone marrow edema (BME) occurs when fluid builds up in your bone marrow. Underlying health conditions, injury or infection cause it. Providers diagnose BME with blood tests, MRI and ultrasound. Treatments include rest, NSAIDs, physical therapy and surgery. BME usually gets better over time. Contents Overview Symptoms and Causes Diagnosis and.
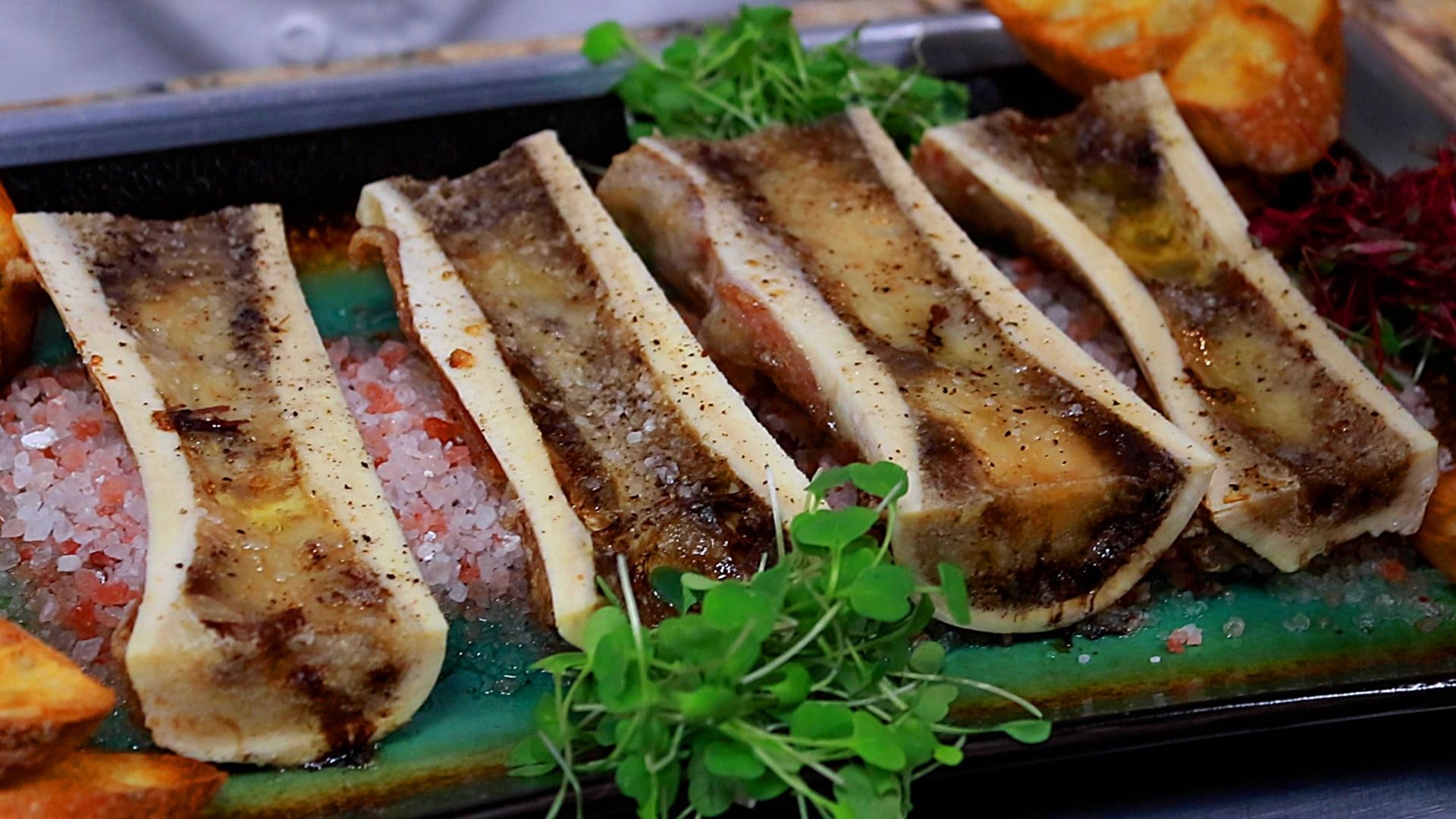

Pork Bone Marrow ubicaciondepersonas.cdmx.gob.mx
Bone marrow edema is an area of increased fluid inside the bone. Causes of bone marrow edema include: Stress fractures. Stress fractures occur with repetitive stress on the bones. This can occur.
BONE, BEEF FEMUR MARROW SPLIT 6″ 134 RAW FROZEN CANOE CUT 60 COUNT
Function. Bone marrow serves a crucial function for the body, producing bone marrow stem cells and blood products. The process of the bone marrow creating red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets is called hematopoiesis. There are two main types of bone marrow, and they each perform specific roles.

What Are the Pros and Cons of a Bone Marrow Transplant for Leukemia?
The femur is the longest, heaviest, and strongest human bone. At the proximal end, the pyramid-shaped neck attaches the spherical head at the apex and the cylindrical shaft at the base. There are also two prominent bony protrusions, the greater and lesser trochanter, that attach to muscles that move the hip and knee. The angle between the neck and shaft, also known as the inclination angle, is.

Bone Marrow Collection and Examination VCA Animal Hospital
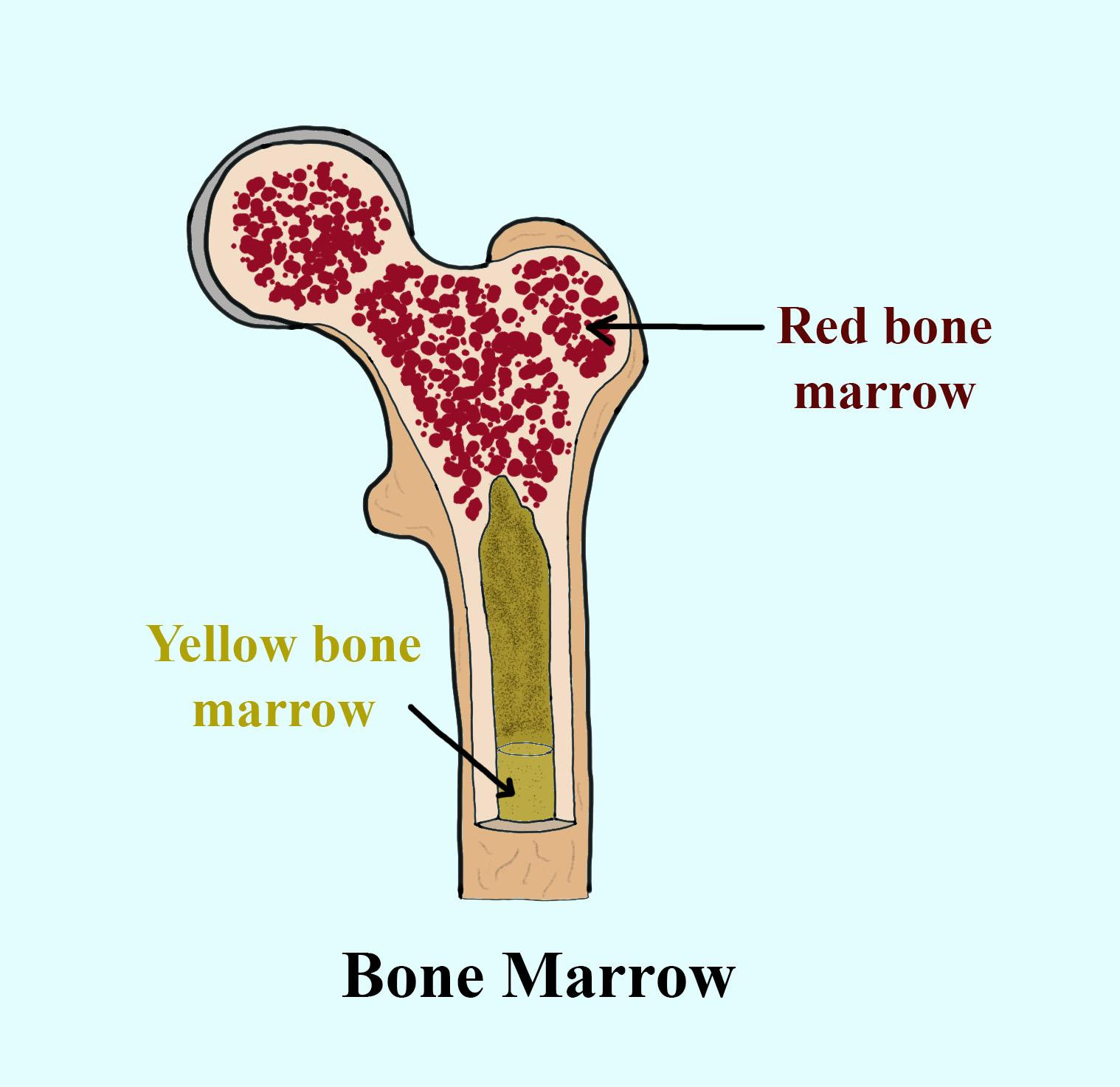
Bone marrow is the soft tissue in your bones that makes and stores blood cells. There are two types of bone marrow. Red bone marrow. This type of bone marrow is found mostly in your flat bones.
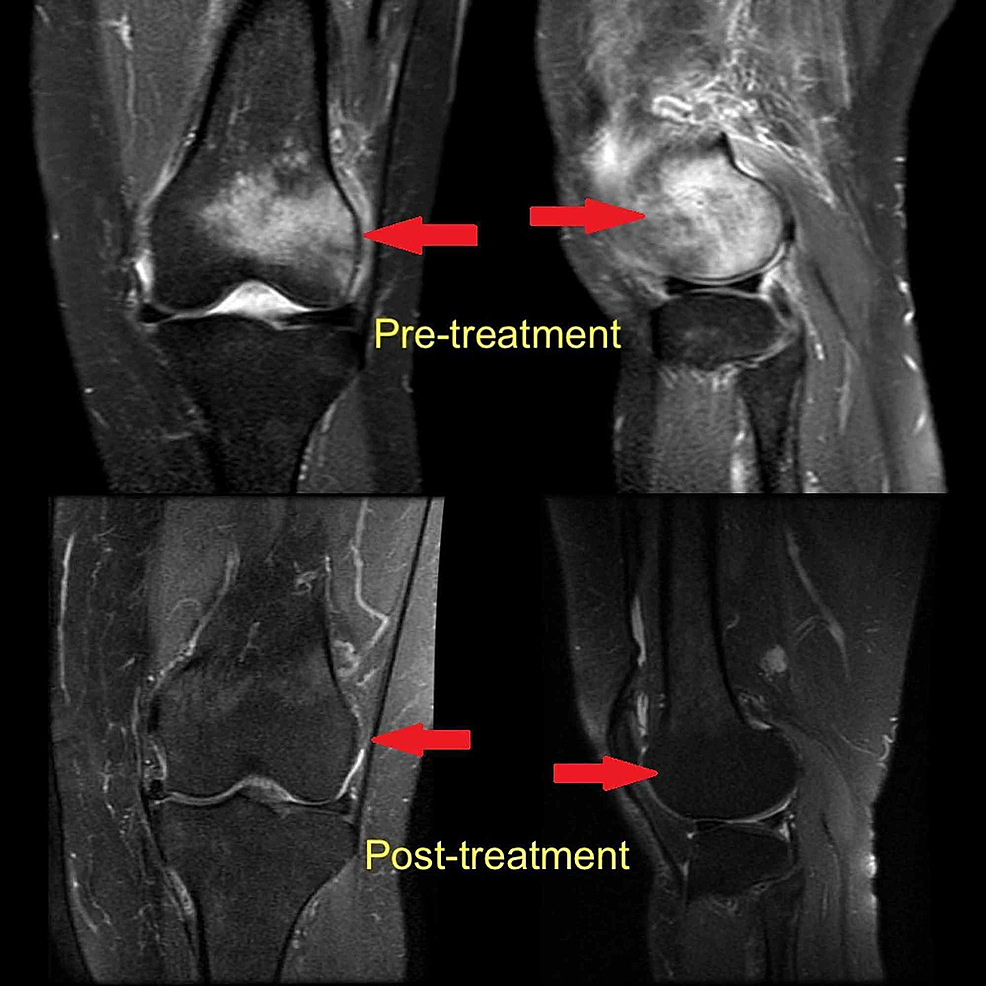
Cureus Effectiveness of Iloprost in the Treatment of Bone Marrow Edema
Bone marrow lesions on magnetic resonance (MR) imaging are common and may be seen with various pathologies. The authors outline a systematic diagnostic approach with proposed categorization of various etiologies of bone marrow lesions.. In long bones, such as humerus and femur, crescentic subchondral area of residual red marrow is commonly.

Figure 3 from Bone marrow reconversion imaging of physiological
g, Femur bone marrow from an 18-month-old Oln mT/+ mouse showing an arteriole surrounded by Oln-mTomato + cells (arrowhead) and an arteriole lacking Oln-mTomato + cells (arrow) in the diaphysis.

Bones Biology 3 with Dr.j at Pasadena City College StudyBlue
Primary Lymphoma of Bone. Lymphoma is a cancer that arises from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Although most lymphomas begin in the lymph nodes, the condition can start anywhere in the body. Primary lymphoma of bone (PLB) starts in bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside most bones. PLB is very rare, accounting for only about 3% of all.

Diagramme infographique de la Moelle osseuse image vectorielle de
Alterations in bone marrow signal are encountered on a daily basis when interpreting MRI of the extremities. Distinguishing benign from malignant entities requires a thorough understanding of the pathologic processes that occur in the extremities. Disease entities can be broadly grouped into the categories of normal marrow or marrow.

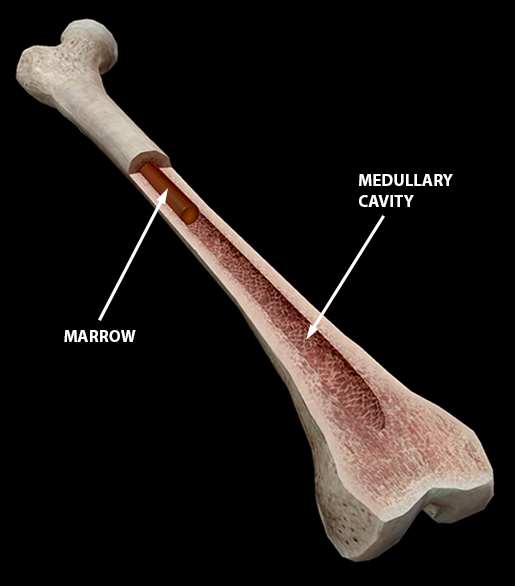
Cross section of the head of the femur showing normal bone marrow
The most common types of benign bone tumors include: Enchondroma: This type of tumor starts in the cartilage. These tumors are found inside the bone, in the marrow space. Osteochondroma: This type of tumor is made up of cartilage and bone and can get bigger while the skeleton is growing. These tumors grow outside the bone.
The red bone marrow occurs in(a)Ribs(b)Ribs and sternum(c)Ribs and
Latin : Medulla rubra ossis. Definition. Red bone marrow is the hematopoietically active unit of bone marrow that gives rise to all types of blood cells. Location. < 5 years of age: All bones. > 5 years of age: Axial flat bones (cranial bones, clavicle, sternum, vertebrae, bony pelvis) and proximal ends of humerus and femur. Histological features.
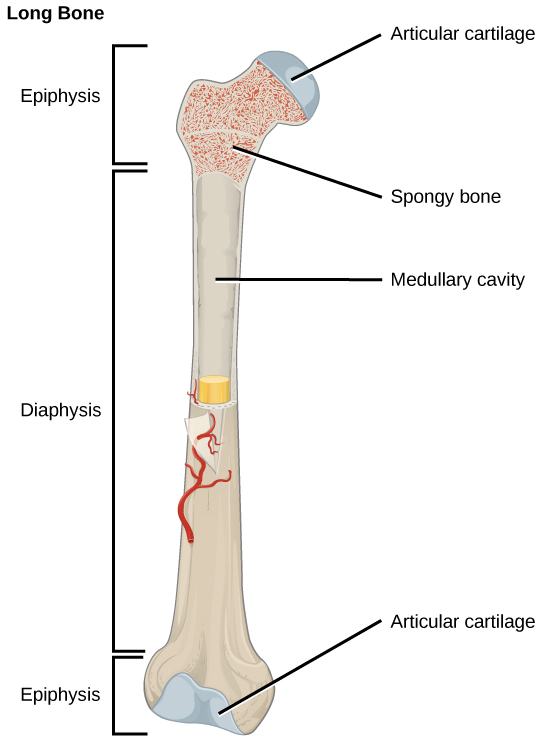
19.2 Bone Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
The femur is the thigh bone and is the largest bone in the human body. A fractured femur can be life-threatening due to blood loss. Learn more about its anatomy, function, and treatment options from Verywell Health, a trusted source of health information. You can also explore other topics related to the skeletal, nervous, and respiratory systems, as well as common skin and liver conditions.
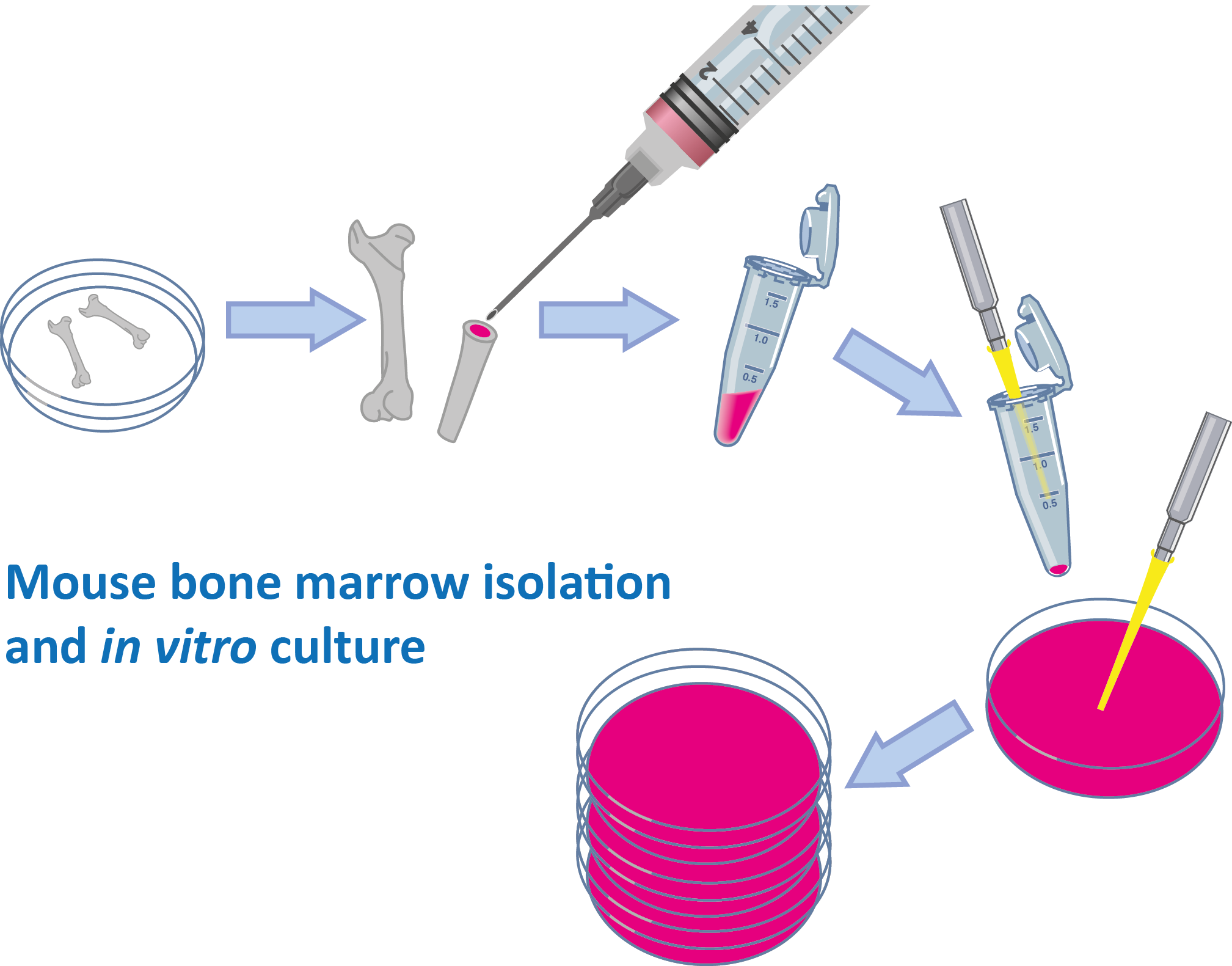
bone marrow isolation and culture mybioscience scientific illustrations
Bone marrow isolated from the femur. Bone marrow was extracted by the processing of the femoral shaft of 10 patients at the age of 28-65 years, undergoing total hip arthroplasty, following a protocol previously established in our laboratory. To fit and fixate the hip prosthesis stem, the femoral canal is opened and prepared with rasps.

Unusual manifestation of ErdheimChester disease BMC Gastroenterology
The bone marrow is the spongy tissue on the inside of your bones. It produces blood cells and later becomes responsible for storing fat and certain stem cells. A bone marrow malfunction is related.

Bone Structure (Femur) Yellow Bone Marrow, Femur Bone, Arteries
In mice, intravital imaging of bone marrow in areas close to the bone cortex has been performed either in the calvarium 11,12,13, in the tibia 3, 14, or in the femur 15, 16. The calvarial.
3D Skeletal System Compact Bone, Spongy Bone, and Osteons—Oh My!
Bone marrow is a spongy, soft tissue that resembles a jelly or jam that you would spread on toast. It comes in two colors, red and yellow. Bone marrow fills the cavities of your bones and holds cells that create red and white blood cells and platelets, which make whole blood. The color of red bone marrow is the result of red blood cell production.